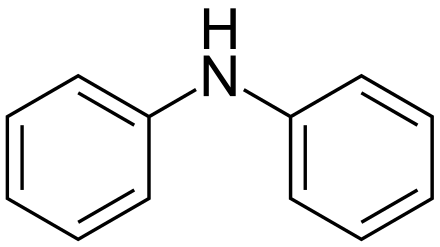
Diphenylamine - DPA
Diphenylamine is a colorless solid, but commercial samples are often yellow due to oxidized impurities. Diphenylamine also dissolves well in many common organic solvents, but is insoluble in water. It is used mainly for its antioxidant properties.Product Details |
|
|---|---|
Formula: |
C12H11N |
CAS Number: |
122-39-4 |
Also Known As: |
N-Phenylbenzenamine; DPA; N,N-diphenylamine; Phenylbenzenamine |
Structure: |
|
applications:
Diphenylamine is a plant growth regulator used post-harvest to control storage scold on apples. It has applications in mining and energy related products. Diphenylamine derivatives are also useful. Ring-alkylated derivatives of diphenylamine are used as "antiozinates" in the manufacture of rubber products, reflecting the antioxidant nature of aniline derivatives.Typical Specifications
Data is representative of average lots;
data taken from specific lots may vary.
Appearance |
Colorless solid |
Boiling Point, °C |
302 |
Density, g/cm3 |
1.2 |
Flash Point, °C |
152 |
Melting point, °C |
52.60 |
Molecular weight, g/mol |
169.22 |
Odor |
Floral odor |
Purity, % |
99.5 |
Refractive index, n20/D |
1.5785 |
Get a Quote?
We want to hear from you and will respond promptly


Distribution Locations Across USA